JMM
JMM:定义线程和内存的交互方式 多线程读取共享变量会存在一个工作内存(高速缓存)
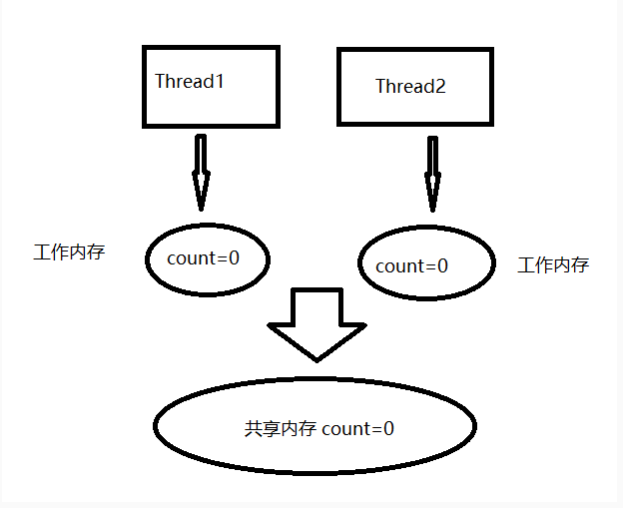
并发编程的有三个概念,包括***原子性、可见性、有序性***。 原子性:要么成功要么失败,原子是最小的单位。 i++; 包含三个步骤:读取 i=0、执行运算、写入 i 的值。
可见性:对应就是 JMM 内存在工作内存中是否可见。保证可见性就能保证实时和共享内存同步。
有序性:是指代码执行的有序性,因为代码有可能发生指令重排序(Instruction Reorder)。
volatile :保证变量的可见性,不保证原子性。代表着实时从共享内存中读取。同时禁止重排序。但是不保证程序代码的执行顺序。
synchronize:在单线程中执行代码,无论指令是否重排,最终的执行结果是一致的。从而保证了原子性。
解决 JMM 也就是说多线程并发的问题。
案例1
class SyncThread implements Runnable {
private int count;
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
// synchronized (this) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count++));
Thread.sleep(100);
// }
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
SyncThread s = new SyncThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(s);
Thread t2 = new Thread(s);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
每次的结果不一定是1000,总小于10.原因是因为多线程的内存可见性。 run方法使用锁可以解决这个问题。牺牲性能。
案例2
class SyncThread implements Runnable {
private int count;
AtomicInteger count1 = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
// synchronized (this) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count1.getAndIncrement()));
Thread.sleep(100);
// }
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
SyncThread s = new SyncThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(s);
Thread t2 = new Thread(s);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
count++ 是一个复杂的操作,原子类可以把他们变成原子。
案例3
class SyncThread implements Runnable {
private int count;
AtomicInteger count1 = new AtomicInteger(0);
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
lock.lock();
// synchronized (this) {
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count1.getAndIncrement()));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (count++));
Thread.sleep(100);
// }
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
SyncThread s = new SyncThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(s);
Thread t2 = new Thread(s);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
使用 JUC 的锁 ReentrantLock,需要手动释放。
